If you noticed that the Antimalware Service Executable process takes up a high CPU on Windows, rest assured – you’re not alone. Many Windows users also report this problem. More importantly, you can fix this problem by yourself without asking a technician for help.
In this article, you’ll learn what Antimalware Service Executable exactly is and how to fix its high CPU usage issue.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
You may know Windows Defender in your Windows, it’s an antivirus software built in Windows. Antimalware Service Executable is one of the background-running services in Windows Defender. It’s also known as MsMpEng.exe, you can find this on the Details tab in your Task Manager.
Antimalware Service Executable is running to scan the malware and spyware when you access them. It will detect if there’s anything harmful. Besides, it also takes a background scan of your system for any viruses or worms. Its scanning relies heavily on your computer’s CPU, that’s why you find it’s eating the CPU usage on your Windows. Couldn’t we solve this problem for the safety of our Windows? No, you can solve it. Move on to the next part, please.
Fixes for ‘Antimalware Service Executable high CPU‘:
- Change Windows Defender’s schedule
- Add Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender exclusion list
- Check Real-time protection settings
Fix 1: Change Windows Defender’s schedule
The error is mainly due to its real-time protection feature. So we can change Windows Defender’s schedule to fix it.
- On your keyboard, press the Windows logo key and R at the same time to invoke the Run box. Type taskschd.msc and press Enter.
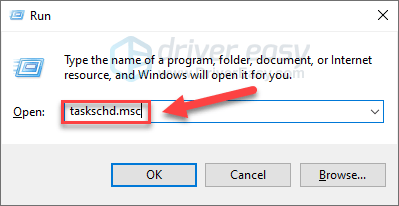
- Double-click on Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows.
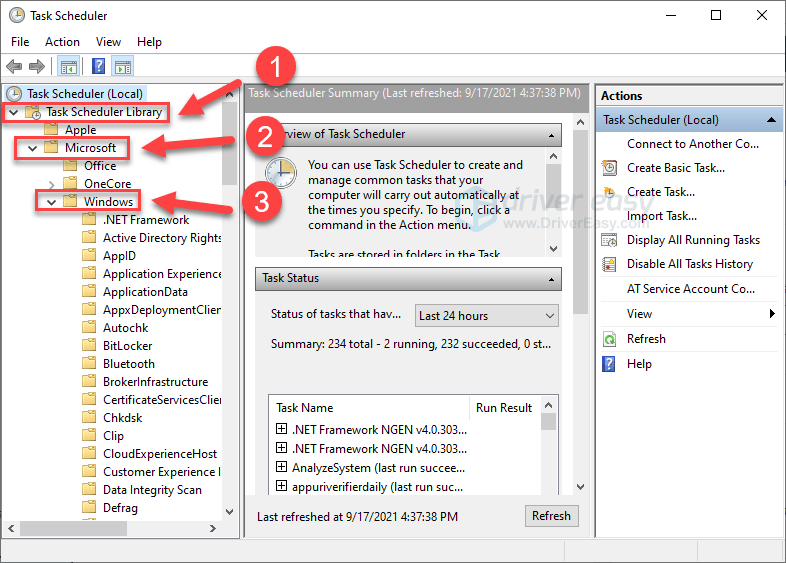
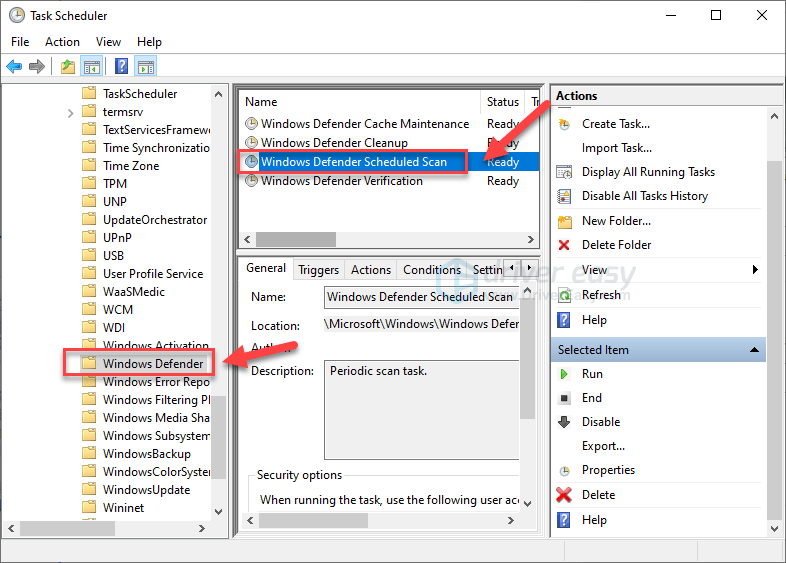
- Double-click Windows Defender in Windows. Then double-click Windows Defender Scheduled Scan.
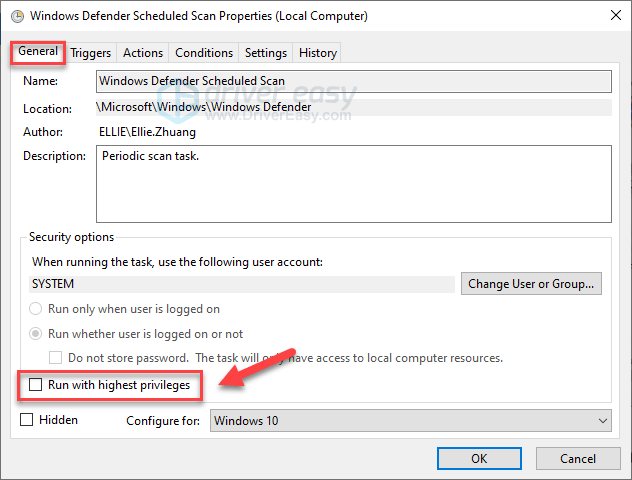
- Uncheck Run with highest privileges.
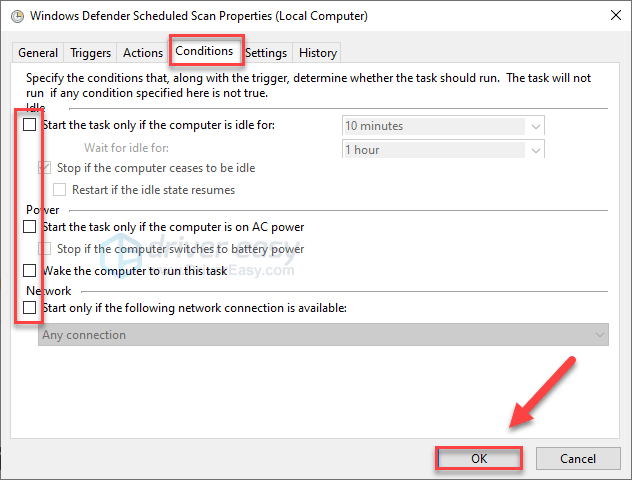
- Uncheck all the items in the Conditions section. Then click OK.
- With the steps above, your error should be fixed now.
If unfortunately, it doesn’t work, please don’t be frustrated, try the following method.
Fix 2: Add Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender exclusion list
High CPU usage can signal issues with Windows Defender real-time scanning. A troubleshooting step is to add the Antimalware Service Executable to Defender’s exclusion list. This prevents scanning of the file, potentially stopping unnecessary scans causing high CPU.
Below we’ll show you how to do this.
- On your keyboard, press the Windows logo key to open the Start menu. Type virus, and click Virus & threat protection from the list of results.
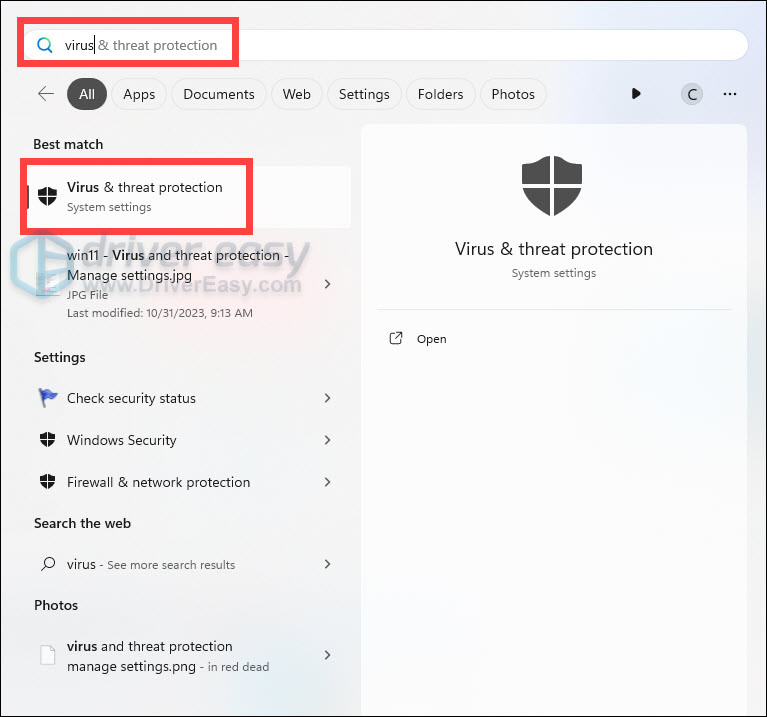
- Find Manage settings under Virus & threat protection settings and click on it.
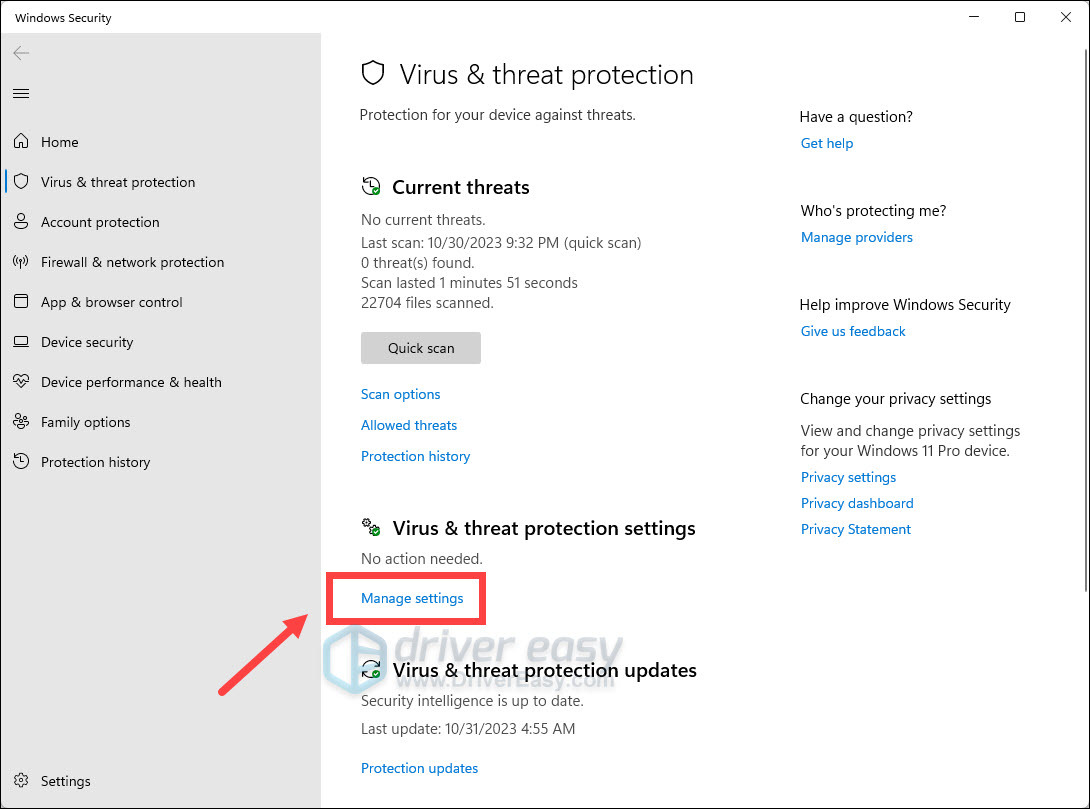
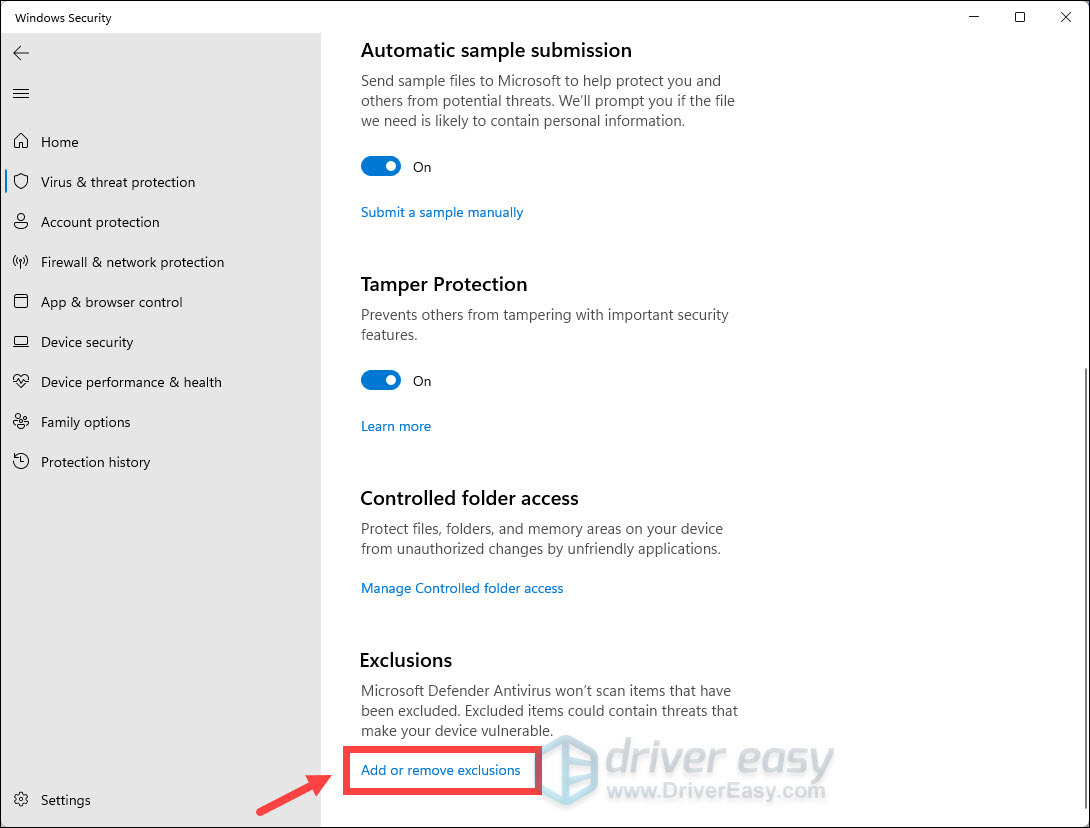
- Scroll to the bottom and click Add or remove exclusions.
- When you’re asked for permission, click Yes to proceed.
- Click Add an exclusion. From the drop-down menu, select Folder.
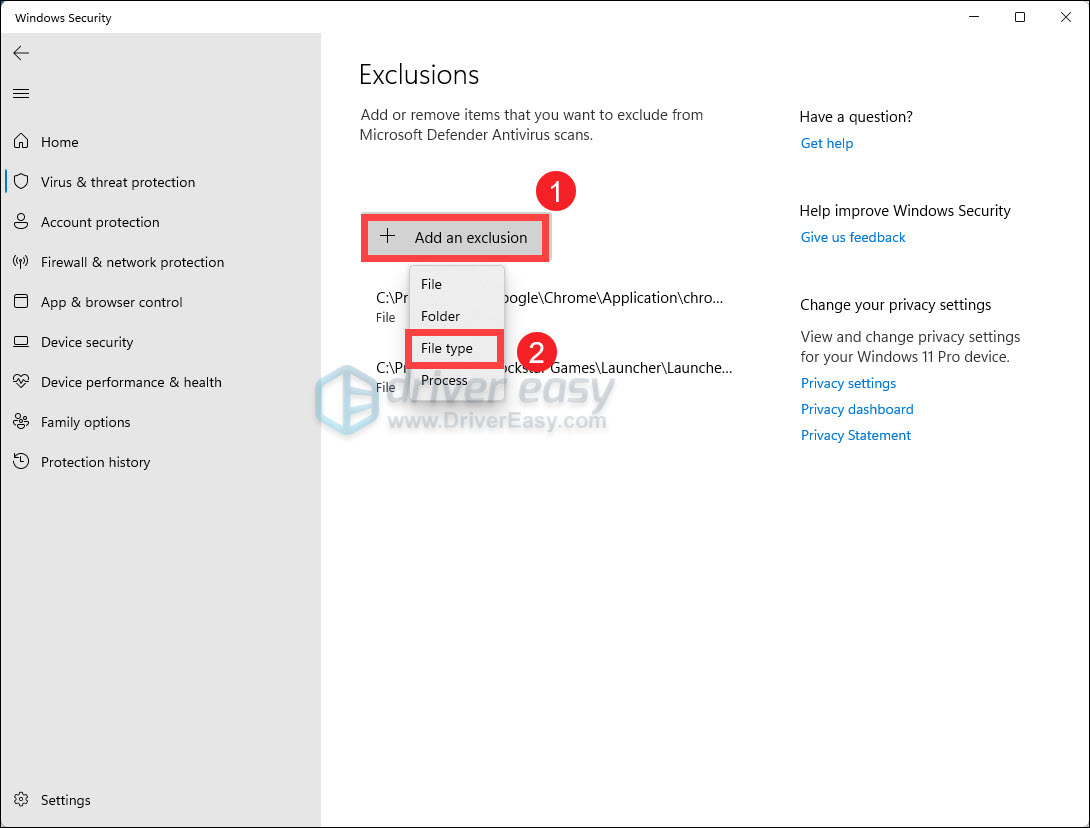
- Then select the following path:
C:\Program files\Windows Defender
Then restart your computer and check if it still consumes high CPU and RAM resources.
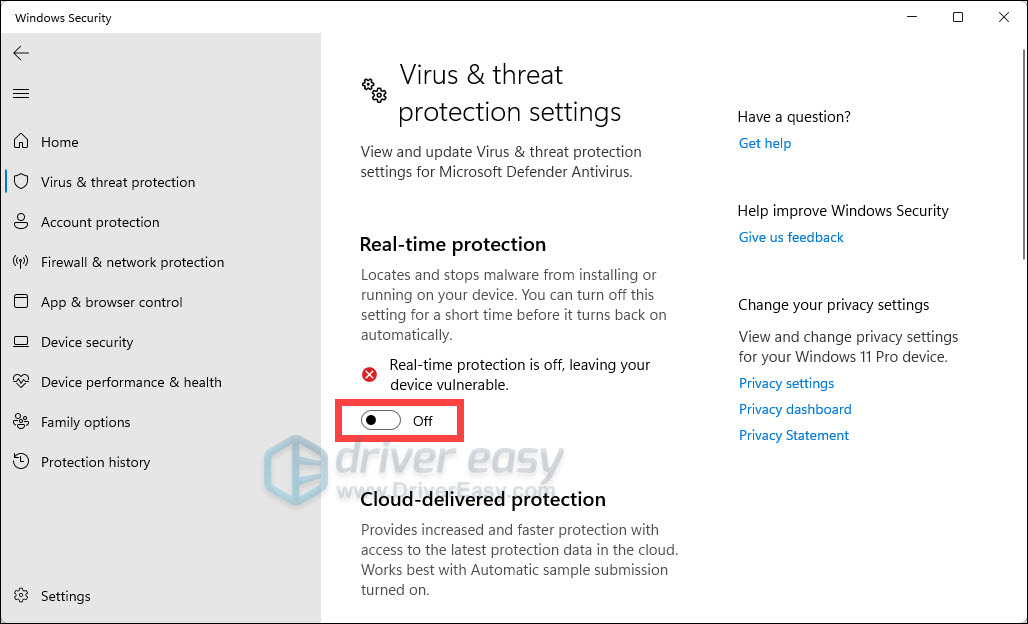
Fix 3: Check real-time protection settings
Another workaround for this issue is turning off the real-time protection.
- On your keyboard, press the Windows logo key to open the Start menu. Type virus, and click Virus & threat protection from the list of results.

- Find Manage settings under Virus & threat protection settings and click on it.

- Scroll a little bit and click on the switch to turn Off Real-time protection.
Still Running Slow?
If, after trying the above, your PC is still running slow, we highly recommend you scan your Windows OS for faulty files or missing system components.
System File Checker is a Windows built-in tool that can help you scan for and repair any corruptions of your system files. Follow the instructions to see how to use it:
- Press the Windows logo key and R on your keyboard to invoke the Run box.
- On your keyboard, type cmd and press Ctrl, Shift and Enter at the same time to run Command Prompt as administrator.

- You’ll be prompted for permission. Click Yes to open Command Prompt.
- Type sfc/scannow, then press Enter.

- The System Files Checker tool will automatically scan for corrupt or missing files and fix them, if there’s any.

- Restart your PC to see if the problem persists.
That’s it for this guide. Hopefully, it helped. Feel free to leave a comment below if you have any questions or suggestions.