The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of your computer and handles running programs and tasks. When the CPU usage is too high, your computer can slow down, freeze, crash, or overheat. This guide will explain what causes high CPU usage and provide detailed, easy-to-follow steps to lower it.
What is CPU Usage?
CPU usage refers to the percentage of your CPU’s processing capacity being used by active programs and background tasks. You can view this percentage in the Task Manager.

How Much CPU Usage is Normal?
When evaluating if your CPU usage is abnormally high, it helps to know what the typical usage ranges are for different tasks:
- Idle: Less than 5% when doing nothing on the desktop. Just background processes running.
- Light use: 5-20% during general browsing, office work, and lightweight programs.
- Heavy use: 50-90% for gaming, video editing, 3D modeling – graphics intensive programs.
- Maxed out: 90-100% when rendering complex videos or 3D visualizations.
Consistently over 90% usage will likely cause performance problems. The goal is to keep it under 90% during normal use.
Causes of High CPU Usage
There are many factors contributing to high CPU usage. Before digging deep into the methods of reducing CPU usage, you should arm yourself with some baseline knowledge about what causes abnormally high CPU usage:
- Too many programs – Having many software apps and browser tabs open divides the CPU power between everything, which can max it out.
- Background Processes – Apps you aren’t actively using can still run tasks in the background and consume resources.
- Outdated Software – Older versions of programs may not utilize your CPU efficiently and demand more power.
- Viruses/Malware – Malicious software runs hidden processes that can secretly eat up CPU capacity.
- Faulty Drivers – Components like graphics cards rely on up-to-date drivers to work properly. Outdated drivers can strain the CPU.
- Overheating – Excessive heat causes devices to work harder and slow down, resulting in higher usage.
How to Lower Your CPU Usage?
Now that you’ve understood the potential causes of abnormally high CPU usage, you can take some steps accordingly to reduce it. Below are some methods you can try.
Method 1 – Restart Your Computer
Restarting your computer is a simple but effective way to reduce CPU usage and tackle various issues. It’s like giving your computer a mini-vacation – a chance to start afresh without the baggage of temporary glitches.
Method 2 – Close Background Programs or Unwanted Applications
Many programs you aren’t directly using can run processes and tasks in the background, eating up CPU resources. Closing unused apps frees up processing power.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open the Task Manager.
- Under the Processes tab, look for any applications you’re currently using and don’t need running in the background.
- Right-click on these processes and select End task to close them.

Things to look for include web browsers, media apps, Microsoft Office programs, launchers, and any other software that starts with Windows but isn’t necessary. However, be cautious not to end any critical processes like your antivirus app. Only close apps you recognize and definitely aren’t using.
Method 3 – Disable Unneeded Startup Programs
Too many programs launching at boot strains the CPU. Definitely disable anything not absolutely essential for startup.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open the Task Manager.
- Go to the Startup tab. Right-click on the programs you don’t need and select Disable.

Method 4 – Update Outdated Software and Drivers
Keeping your software up-to-date improves compatibility with your CPU and fixes bugs that may be causing strain. Outdated drivers can also overload the CPU and cause conflicts.
Software Updates:
- Check the software vendor’s website for the latest updates.
- Follow the on-screen prompts to download and install updates.
- Restart your computer after updating.
Driver Updates:
Device drivers act as the communication bridge between your hardware components and the CPU. Outdated or corrupt drivers can lead to CPU strain.
You can update drivers manually by visiting each device manufacturer’s website and downloading the latest versions. However, this can be time-consuming.
A quicker way is to use an automated driver update utility like Driver Easy. This scans your computer, identifies any outdated drivers, and downloads the newest versions, direct from each manufacturer.
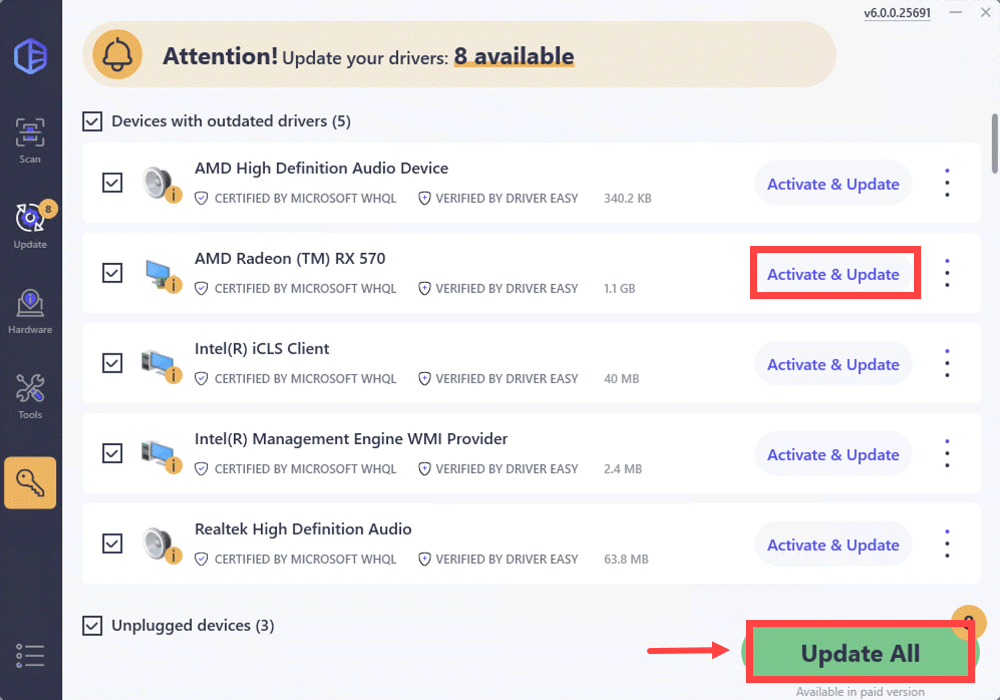
To update drivers with Driver Easy, simply download the software and launch it. Click Scan Now, and Driver Easy will scan your computer and detect any devices with missing or outdated drivers.
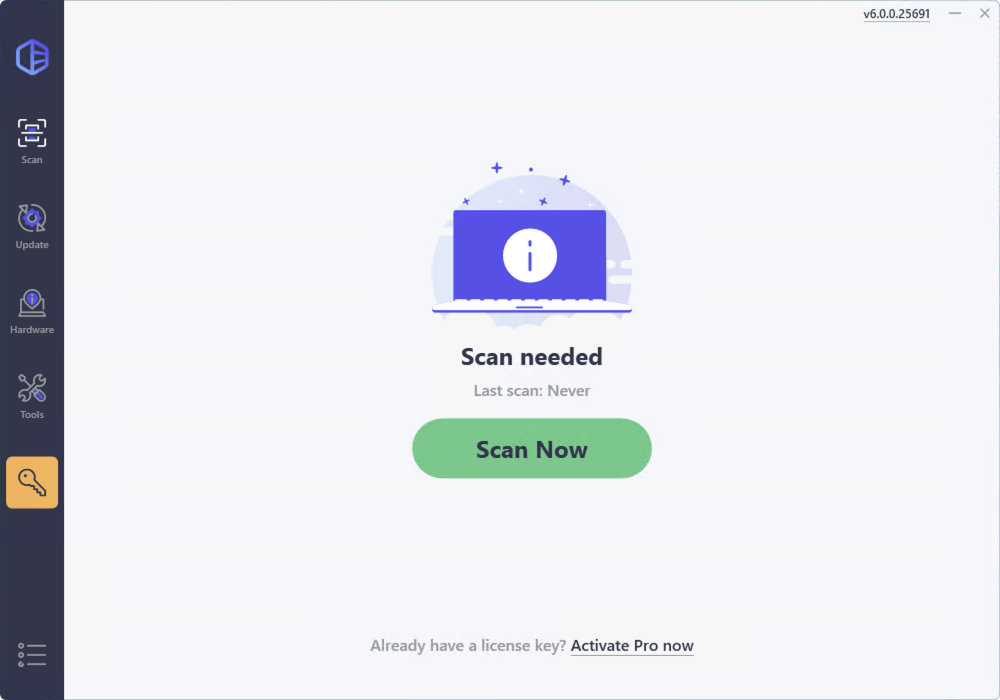
Click the Activate & Update button next to any flagged device or click Update All to update all the outdated drivers. You can sign up for the free trial to update drivers with no upfront cost.
If, for any reason, Driver Easy does not meet your expectations, and you request a refund within 30 days of purchase. Should you require any assistance, feel free to contact Driver Easy’s support team at support@drivereasy.com.
Method 5 – Run Antivirus and Malware Scans
Viruses, spyware, ransomware, and other malware are specifically designed to infect computers and misuse system resources. They run hidden processes that secretly overwork your CPU in the background.
Running full scans with trusted antivirus and anti-malware tools can detect and remove any infections or threats lurking on your system. This cleans up malicious programs that may be spiking your CPU usage.
Top antivirus programs like Norton can help detect deeper threats that standard antivirus software might miss. Once you download and install the software, run a full scan by following the on-screen instructions.

Method 6 – Clean Computer Hardware
Dust buildup in your computer can lead to overheating, which causes the CPU and other components to run slower and work harder. Regularly cleaning your computer improves airflow and cooling efficiency.
Method 7 – Check for Corrupted System Files
Corrupted or damaged Windows system files can cause conflicts and errors that force the CPU to work harder, spiking usage. Running scans to check for problems and repairing any found can help optimize performance.
The System File Checker (SFC) is a utility built into Windows that can scan for and repair corrupted system files:
- Open the Start menu, type cmd.
- Find Command Prompt, then click Run as administrator.

- Type sfc /scannow and hit Enter. This will scan Windows files.

- If damaged files are found, run DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth to repair them.

Method 8 – Reinstall Windows
If no other methods have worked, reinstalling Windows may fix software-related issues causing the problem.
Try restoring from a system restore point first if you have one from before the CPU usage spikes began.
If that doesn’t help or you don’t have an applicable restore point, you can reinstall Windows to completely reset the software and system files.
Before reinstalling:
- Backup personal files and data to external storage or the cloud in case they are deleted.
- Windows lets you choose to keep personal files or delete everything when reinstalling.
To reinstall Windows 10:
- On your keyboard, press the Windows logo + I keys simultaneously to open Settings.
- Select Update & Security.

- Select Recovery from the left navigation panel. Then you should see Reset this PC. Click on the Get started button. Then follow the on-screen instructions to proceed.

To reinstall Windows 11:
- In the Windows search bar, type Reset this PC.
- Choose your desired reset option – keeping apps, files, and settings or not.
- Allow Windows to complete the reinstallation process.
So that’s the full guide on how to reduce CPU usage. Hope you find it helpful! If you have any questions, drop us a line in the comment section below. We’ll get back to you ASAP.